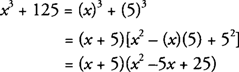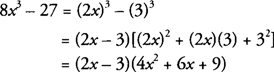- Difference of two squares
- a2- b2 = (a + b)(a - b)
- (a-5)(a+5)
- (x-10)(x-10)
- (y-18)(y+18)
- Trinomial perfect squares
- x² + 6x + 9 = (x + 3)²
- x² − 4x + 4 = (x − 2)²
- x² − 4x + 4 = (x − 2)²
- Sum of two cubes
- a3 + b3
- 3 - cube root 'em
- 2 - square 'em
- 1 - multiply and change
- a3 + b3
- Sum of two cubes
- a3 - b3
- 3 - cube root 'em
- 2 - square 'em
- 1 - multiply and change
125 − x3=(5 − x)(25 + 5x + x2)
1 − a3=(1 − a)(1 + a+ a2)
- a3 - b3
- Binomial expansion
- (a + b)3 = Use the pattern
- (a + b)4 = Use the pattern
(2x + 3y)4 =16x 4 +96x 3 y + 216x 2 y 2 +216xy 3 +81y 4